Do you want to talk about experiences you’ve had, tell a good or funny story, or talk about something you regret in the past?
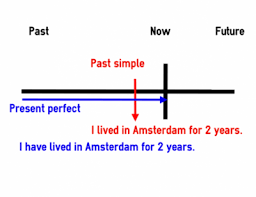
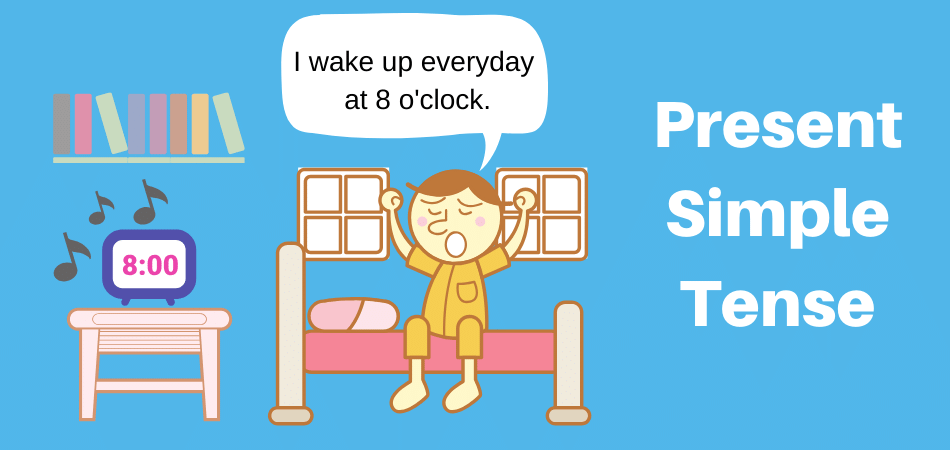
We use the present perfect for something that started in the past and continues in the present:
- We have lived here since 2017. [and we still live here]
- I have been working at the university for over ten years.
We also use it for something that happened in the past but is important in the present:
- I can’t open the door. I‘ve left my keys in the car.
- Jenny has found a new job. She works in a supermarket now.
Be careful! We do not use the present perfect with words which refer to a finished past time:
- I have seen that film
yesterday. - We have just bought a new car
last week. When we were childrenwe have been to California.
But we can use the present perfect with words which refer to a time which is not yet finished:
- Have you seen Helen today?
- We have bought a new car this week.
However, as soon as you mention a time, you need to switch to a past tense. For example:
- I went windsurfing three years ago.
- I didn’t drink a lot last night.
- Did you eat a lot of sushi when you were in Japan?
For this reason, when you’re talking about life experiences, you often start with the present perfect, and then switch to a past tense when you mention a specific time.
For example, someone might ask you, Have you ever been to Australia?
You might answer, Yes, I went there two years ago, for my friend’s wedding.
The question is present perfect, because it’s asking about experiences without mentioning a time. The answer mentions a time—two years ago—and so you need the past simple.

There are past structures which you can use to show a difference between the past and the present:
USED TO
You can use used to to talk about something which was true in the past, but isn’t true now. For example:
- He used to have a beard. –> He had a beard in the past, but he doesn’t have one now.
- I used to live in Berlin. –> I lived in Berlin in the past, but I don’t live there now.
You can also use the negative form—didn’t use to—to talk about things that weren’t true in the past, but are true now. For example:
- They didn’t use to get on so well. –> They didn’t get on well in the past, but they do now.
- I didn’t use to wear glasses. –> I wear glasses now, but I didn’t in the past.
You can also make questions:
- Did you use to play a musical instrument?
- Didn’t he use to work here?
WOULD
You can also use would to talk about actions or habits which you did in the past, but you don’t do now.
Would is the past tense of will. We use it when we talk about the future in the past. For example:
- He thought he would buy one the next day.
- Everyone was excited. The party would be fun.
WAS/WERE GOING TO
Was/were going to, also refers to the future in the past:
- John was going to drive and Mary was going to follow on her bicycle.
- It was Friday. We were going to set off the next day.
We also use the past continuous to talk about the future from a time in the past.
- It was September. Mary was starting school the next week.
- We were very busy. Our guests were arriving soon and we had to get their room ready.
ANY MORE
Finally, you can also use a present verb plus any more. This has a similar meaning to used to. Let’s look:
- She doesn’t live here any more. –> She lived here in the past, but she doesn’t live here now.
- I don’t have time to listen to music any more. –> I had time in the past, but now I don’t.
‘SET THE SCENE’ WITH PAST CONTINUOUS
‘SET THE SCENE’ means you need to describe the background of the story. What was happening at the start of the story? Who was there, and what were the people in your story doing at the start?
To give background to a story, you use the past continuous. For example:
- We were sitting on the bus, ready to leave.
- It was raining so hard you couldn’t even see out of the window.
This isn’t just useful when you’re telling long stories; you can use this any time you’re giving a slightly longer answer about the past.
However, if you do want to tell a longer story, there are some other things you’ll need to know.
SHOW THE SEQUENCE OF EVENTS IN THE PAST
When you start a story, you usually say when these things took place. You’ll say something like:
- Last week…
- This happened two years ago, in summer.
- So, yesterday, I was walking down the street…
This time reference ‘fixes’ the time when your story starts.
PAST PERFECT
We use the past perfect when we are looking back from a point in the past to something earlier in the past.
For example:
- Helen suddenly remembered she had left her keys in the car.
- When we had done all our shopping, we caught the bus home.
- They wanted to buy a new computer, but they hadn’t saved enough money.
- They would have bought a new computer if they had saved enough money.
Use the past perfect to talk about things that happened before the start of the story.
Let’s see another example:
- When I was 25, I quit my job and decided to train as a pilot. I had always wanted to learn to fly.
Here, you have a time reference which ‘fixes’ the start of the story: when I was 25.
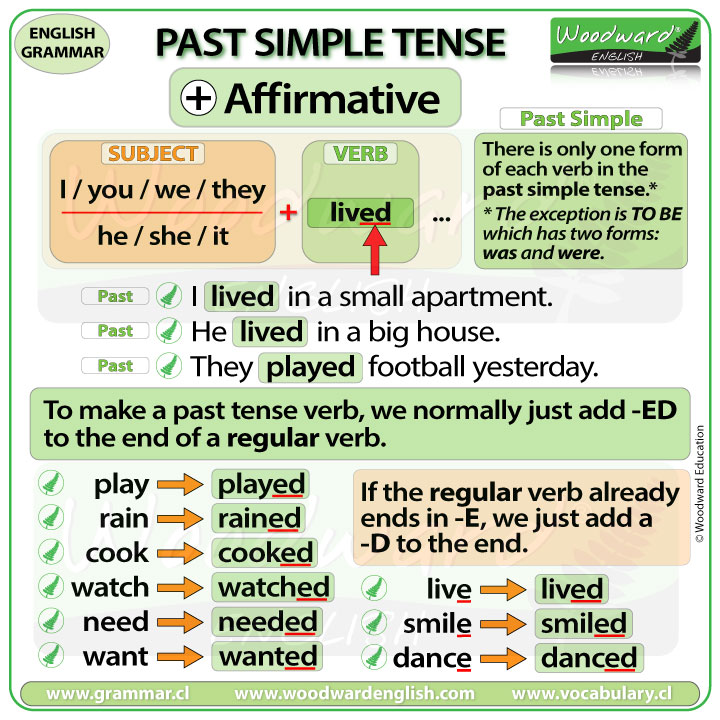
If you’re talking about the events of your story, just use the past simple, like this:
- We drove out of the test centre.
- We sat in a traffic jam for ages.
- I had a small accident on the way home.
Using these verb tenses, you can make it clear when things happened in the past, and whether something happened before or after something else.
THE PAST WITH MODAL VERBS
Could – the past tense of can:
- You could get a good meal for a pound when I was a boy.
Would – the past tense of will:
- He said he would come but he forgot.
May have, might have and could have
To show that something has possibly happened in the past:
- I’ll telephone him. He might have got home early.
- She’s very late. She could have missed her train.
Should have – the past form of should
- I didn’t know he was ill. He should have told me.
- You shouldn’t have spent so much money.
Would have and could have
We use would have and could have to talk about something that was possible in the past but did not happen:
- I could have gone to Mexico for my holiday but it was too expensive.
- I would have called you, but I had forgotten my phone.
- They would have gone out if the weather had been better.
TALKING ABOUT REGRETS IN THE PAST
There are three different forms you can use to talk about regrets in the past:
Wish
You can use wish plus the past perfect to talk about something you regret. For example:
- I wish I’d learned other languages when I was younger.
- I wish I hadn’t said that.
Remember that here you’re talking about the opposite of what really happened. If you say I wish I hadn’t said that, you did say something in reality, and now you regret it.
If only
You can also use if only plus the past perfect, like this:
- If only I’d kept my Spanish going.
- If only I hadn’t wasted so much time.
The meaning is very similar to wish: you did something, or didn’t do something, in the past, and now you regret it.
Could have
Finally, you can sometimes use could have to express regrets in the past, often as part of a longer if-sentence. For example:
- I could have tried harder.
- If I hadn’t left things to the last minute, I could have passed easily.
Now that you have already seen the words, phrases, and structures you need to talk about the past in clear, fluent English, the next step to improve your conversation and grammar skills is to practice!
Start by testing your understanding of the lesson with this quiz. Next, you can listen to the complete lesson.