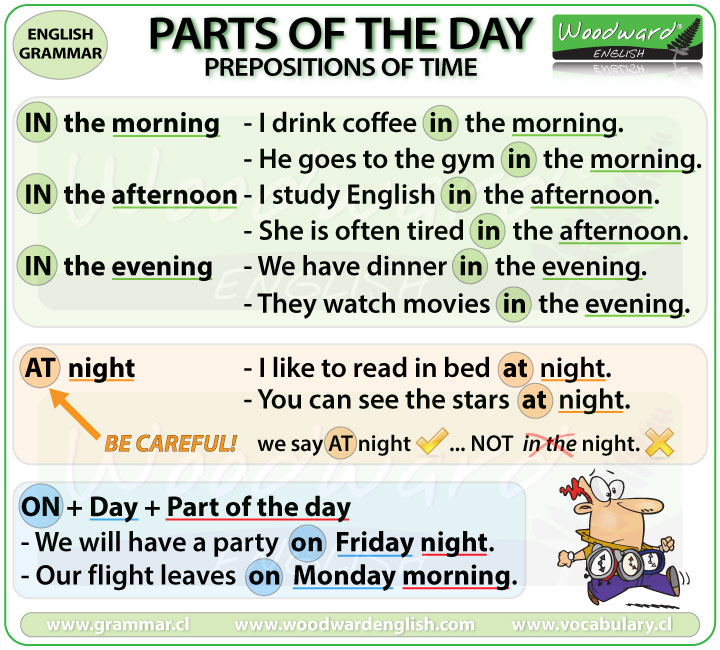
Então, o que são phrasal verbs?
Phrasal verbs são duas ou mais palavras que juntas resultam em uma nova palavra.
Muito comuns no inglês falado, os phrasal verbs podem ser bastante confusos, pois seus significados nem sempre são fáceis de deduzir – e existem milhares deles. Na verdade, muitos phrasal verbs são variações distintas do mesmo verbo base, o que pode causar dúvidas.
Vejamos o phrasal verb get over, por exemplo. O verbo get significa “adquirir”, e a preposição “over” geralmente refere-se a estar mais alto ou acima de algo. No entanto, junte-os, e o phrasal verb get over significa “recuperar” ou “superar”, portanto, um novo significado.
Two-part verbs
São os phrasal verbs formados por um verbo e uma partícula:
- grow + up
The children are growing up.
- take + after
She takes after her mother.
(= She looks like her mother or she behaves like her mother.)
- count + on
I know I can count on you.
(= I know I can trust you or I know I can believe you.)
Inseparable phrasal verbs
Alguns two-part verbs possuem somente um padrão, os inseparable phrasal verbs, ou seja, não podem ser separados:
| Subject | Verb | Particle | Object |
|---|---|---|---|
| The children | are growing | up. | – |
| She | takes | after | her mother. |
| I | can count | on | you. |
Mas outros two-part verbs possuem dois padrões. O usual é o separable:
Separable phrasal verbs
Quando o separable phrasal verb é seguido por um substantivo, podemos separá-lo ou não.
| Noun (subject) | Verb | Noun (object) | Particle |
|---|---|---|---|
| She | gave | the money | back. |
| He | knocked | the glass | over. |
| We | will be leaving | our friends | behind. |
A seguir, os advérbios mais comuns em um phrasal verb, que indicam que ele pode ser separável –SEPARABLE:
Apart, around, away, back , behind, down, out, over, together, off, over, up.
Mas que também aceitam o padrão INSEPARABLE:
| Noun (subject) | Verb | Particle | Noun (object) |
|---|---|---|---|
| She | gave | back | the money. |
| He | knocked | over | the glass. |
| We | will be leaving | behind | our friends. |
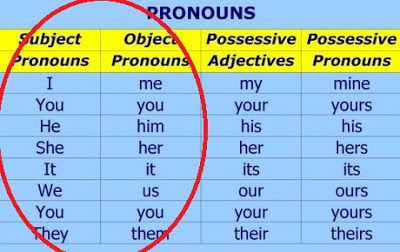
Quando o phrasal verb é seguido por um um PRONOME PESSOAL (I, me, you, we, us), o verbo e a partícula devem sempre ser separados, ou seja, são sempre SEPARABLE:
- She gave it back. (NOT
She gave back it.)
- He knocked it over. (NOT
He knocked over it.)
- We will be leaving them behind. (NOT
We will be leaving behind them.)
Three-part verbs
Alguns verbos são compostos por três partes: um verbo e duas partículas. Eles seguem o padrão INSEPARABLE:
| Noun (subject) | Verb | Particle | Particle | Noun (object) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| His girlfriend | walked | out | on | him. |
| She | caught | up | with | the other runners. |
| Children | should look | up | to | their parents. |
Os phrasal verbs são usados do mesmo modo que um verbo qualquer, ou seja, em qualquer forma ou tempo:
Simple past tense:
- I had the flu last week but got over it.
Infinitive:
- I rested last week to get over the flu.
Gerund:
- I spent last week getting over the flu.
Observe que apenas o verbo é conjugado. A ou as partículas que o seguem, permanecem como são.
Agora vamos praticar?